
AURAL ATRESIA SKIN
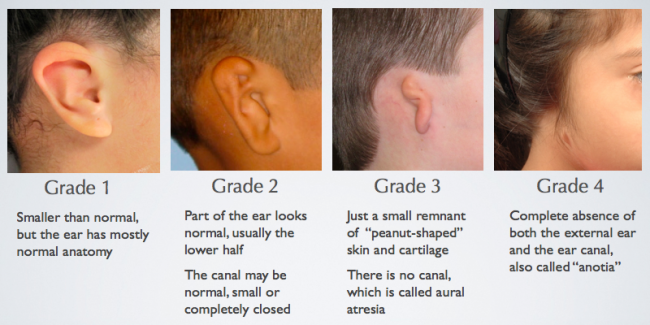
After surgery, cosmetic reconstruction surgery is done using graft material like skin graft from thighs and ribs cartilage. Atresia repair (atresiaplasty) is then performed by creating the ear canal by drilling the atretic plate (abnormal/closed-ear) and forming an eardrum to improve hearing. Microtia (small ear), if present, is treated first by the surgeon. Surgical Repair: Surgical treatment is usually indicated at the age of six to seven years of age. It helps in hearing by transfer of sound from the skull bone to the auditory nerve (hearing nerve). Headband Hearing Device: This device helps to transfer sound waves from the skull bone to the inner ears and is called a “bone conduction sound processor (BCSP).” It is given to children in the early stages of hearing loss in the first month of their life till the age of five years to prevent delay in speech and language development.īone Anchored Hearing Device: These are the titanium devices that are surgically implanted (placed) by the surgeon behind the skull (back of ears) of the child. Various management criteria for aural atresia are: Speech and Language Assessment: It is done by a speech-language pathologist to check for any disturbances in speech and delays in language development.īrainstem Auditory Evoked Response (BAER): It is done to assess the response of a child to the sounds. A thorough physical examination of a newborn in the first few days of life is done for any abnormalities in the development of jaws, head, eyes, spine, ears, and facial nerve function.Ĭomputed Tomographic (CT) Scans: These scans help to detect any abnormalities present in the inner and middle ear like facial nerve involvement, otic (ear) capsule defects, and ear bone connections (incus -stapes bone).Īudiometry (Hearing Test): It is done to check the severity of hearing impairments. The presence of any hearing impairment is ruled out. History: A detailed history of recent trauma to the ears, past ear surgery, frequent external ear infections, and any person in the family with a similar disorder is recorded.Ĭlinical Examination: A complete physical examination of the external ear is done by an ENT (ear, nose, and throat) specialist. What Are the Signs and Symptoms Associated With Aural Atresia?ĭiagnostic criteria for aural atresia are: Type C: Total aural atresia (it involves the complete absence of ear canals with middle ear deformities). Type B: Partial aural atresia (partial formation of bony and fibrocartilage membrane ear canal). Type A: Stenosis (narrowing) of the external ear canal, with a slightly deformed/small but intact tympanic membrane. There are three types of inborn aural atresia based on development are: What Are the Types of Congenital (Inborn) Aural Atresia?

Hereditary: Parents with aural atresia have high chances of having children with similar defects.

Here Is What You Need to Know About Earwax
Genetic Abnormalities: Due to deletion of gene 18q22.3. The right ear is more frequently affected than the left ear.Īssociated With Congenital (Birth) Abnormalities: Like Treacher Collin syndrome (a genetic disorder affecting teeth, jaw, and bones) or hemifacial microsomia (structural defects in jaws, eye socket, and ears).Įxternal Ear Trauma: Like trauma to the ear during road accidents, gunshot injury, or during surgery. It can affect one or both the ears, but in 30 % of cases, it is mostly bilateral (both ears). What Is the Prevalence of Aural Atresia?Īural atresia accounts for one among 15000 births of the general population.Īpproximately 50 % of cases are associated with birth (congenital) abnormalities. Failure of the separation of the mastoid bone (absence of mastoid growth) with the lower jaw leads to aural atresia. During the seventh month of birth, normally, the formation of ear canals is completed, and mastoid bone (part of the temporal bone located behind the ears) grows posteriorly (back) to separate from the mandible (lower jaw). Disturbance in this process results in external ear deformities. The external ear canal is recanalized (hollow out) by the six months of child development. It is sometimes associated with microtia (a child born with a small or missing ear).

It can be acquired or is congenital (present since birth). Aural atresia is a common defect in which there is an absence of patent ear canals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
